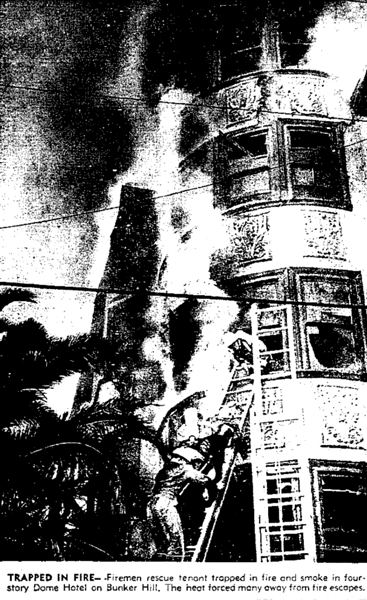They were eastern European immigrants, utterly integrated into the ways of American society. They were doting, loving parents; rarely does television depict such a highly functional family. They were the Munsters, and they existed to teach us valuable, eternal lessons: build hot rods out of hearses and caskets. Let your home be overrun by the Standells and their beatnik buddies. And see that your house is the biggest and spookiest on the block.
They were eastern European immigrants, utterly integrated into the ways of American society. They were doting, loving parents; rarely does television depict such a highly functional family. They were the Munsters, and they existed to teach us valuable, eternal lessons: build hot rods out of hearses and caskets. Let your home be overrun by the Standells and their beatnik buddies. And see that your house is the biggest and spookiest on the block.
Aside from these eternal lessons, the Munsters also represented something particular to their time–to be exact, Sept.‘64-May ‘66. (No, I‘m not talking about that despite their status as affable, upstanding citizens, the average American really didn‘t want to live next door to someone whose skin was a different color.) For our purposes I want to look at another member of the Munster clan, the house itself: 1313 Mockingbird Lane.

 The Munster manse is important to our topic at hand because it represents the attitude toward Victorian architecture at the time the CRA was in its wholesale frenzy of demolition: in a world blooming with Cliff May and Eichler knock-offs, 1313 was an ungainly, awkward embarrassment. It was, to many, nothing if not downright frightening. And those who would live in such a place? They must be odd in the extreme. Beyond curious. Again, frightening: those who dare knock on that door usually end up vaulting themselves over the gate and running down the street in terror. Besides having skin of a different color (in this case, green), the dwellers therein are, in fact, monsters.
The Munster manse is important to our topic at hand because it represents the attitude toward Victorian architecture at the time the CRA was in its wholesale frenzy of demolition: in a world blooming with Cliff May and Eichler knock-offs, 1313 was an ungainly, awkward embarrassment. It was, to many, nothing if not downright frightening. And those who would live in such a place? They must be odd in the extreme. Beyond curious. Again, frightening: those who dare knock on that door usually end up vaulting themselves over the gate and running down the street in terror. Besides having skin of a different color (in this case, green), the dwellers therein are, in fact, monsters.
The Addams Family also had a big creepy house, though it was more a museum (as noted in theme song, of course) than mired in decrepitude. If the Addams examination of landed gentry‘s eccentricities has any bearing on Bunker Hill, it is only in illuminating the Bunker Hill of yore–therein lies no bearing on the Bunker Hill of 1965. (Interestingly, the shot of the Addams house in the first episode was filmed down at 21 Chester Place [and is now, sadly, demolished].)
The house at Chester Place, and its matte-painted addition:


 Nevertheless, while one could view Gomez as a demented Doheny, or a cracked Crocker, perhaps because (Charles) Addams‘s work is so associated with the New Yorker, there‘s something rather East Coast about the Addamses. After all, the Italianate Addams place was modeled after a house from Chas‘s New Jersey boyhood, or a building at U-Penn, depending on whom you ask.
Nevertheless, while one could view Gomez as a demented Doheny, or a cracked Crocker, perhaps because (Charles) Addams‘s work is so associated with the New Yorker, there‘s something rather East Coast about the Addamses. After all, the Italianate Addams place was modeled after a house from Chas‘s New Jersey boyhood, or a building at U-Penn, depending on whom you ask.
There‘s something uniquely Angeleno about the Munsters–when you take the Koach out to Mockingbird Heights drag strip, you can smell the Pomona. The Munsters went to Marineland. Herman hung with Dodger manager Leo Durocher.

1313 was every bit Bunker Hill–dig the deep central Gothic-arched porch, the extensive use of shabby shingle, the patterned chimney. The asymmetrical double porches and widow‘s walk are a nice touch. Its most notable feature might be the spook-faced gable. And inside; no well-intentioned postwar updates there–all spindlework and heavy drapes and art-glass lamps. The crumbling stone gates, the overgrowth”¦this was disrepair in all its Gesamkunstwerkiness. The gag, of course, was that 1313 was the one and only of its kind on the block. The standout. The sore thumb. Bunker Hill was a nest of these things.
Making matters worse, a Munster stood for something. A Munster stood for his home, protecting it with his or her life (undead though they may be). In “Munster on the Move,” (Season 1, Episode 27, airdate March 25, 1965) Herman gets a promotion at the parlor whereby the family must sell the house and move to Buffalo. Grandpa inadvertently sells to a wrecking company; when the Munsters find out the house‘s fate, they put the good of the house before their own self-interest. When the bulldozers show up, the family is out front, cannons packed with Grandma‘s best silver. The head of the wrecking crew shakes his head in disgust, but not disbelief; says it reminds him of the little old ladies who threw themselves in front of the bulldozers when they were tearing down their homes for the freeway system. “Look Jack, I bought this place to wreck it and put in a parking lot. Now move it, because we‘re coming through.” After the wreckers see that Herman can swing a wrecking ball around, they turn tail and flee.
Wreckers arrive:

Herman reasons with them to great effect:

Bunker Hill had its Frank Babcock, but even he was no Herman Munster.
One last thing. In “Herman Munster, Shutterbug,” (Season 2, Episode 4, October 7, 1965) Herman inadvertently snaps a photo of two bandits running out of the Mockingbird Heights Bank. And where do these bank-robbing low-lifes lay low? We see in an establishing shot that they‘re staying at “The Grand”–

–which we of course we know as none other than the Dome.

Dome Image, Arnold Hylen Collection, California History Section, California State Library; postcards, author; everything else courtesy the beneficent glow of the CRT



 After our initial report on
After our initial report on 



 March 11, 1961. Alfred Carrillo, 33, was a Dome resident in good standing who had the bad luck to be sitting in a bar at 301 South Hill Street one early Friday morning. Victor F. Jimenez, 26, unemployed truck driver, shot Alfred and then drove off, later to be arrested at his home. (The bar at 301 South Hill, by the way, was the bar at the base of Angels Flight–seen here with Lon Chaney Jr. in the 1956 outing
March 11, 1961. Alfred Carrillo, 33, was a Dome resident in good standing who had the bad luck to be sitting in a bar at 301 South Hill Street one early Friday morning. Victor F. Jimenez, 26, unemployed truck driver, shot Alfred and then drove off, later to be arrested at his home. (The bar at 301 South Hill, by the way, was the bar at the base of Angels Flight–seen here with Lon Chaney Jr. in the 1956 outing 

 The history of Bunker Hill could not be written without mention of a man who stood up to face the foe. Who fought City Hall; who fought the law, and sure, the law won. But let‘s remember the man. Firebrand. Gadfly. Babcock.
The history of Bunker Hill could not be written without mention of a man who stood up to face the foe. Who fought City Hall; who fought the law, and sure, the law won. But let‘s remember the man. Firebrand. Gadfly. Babcock. But one fellow didn‘t think the idea so all-American–owner of
But one fellow didn‘t think the idea so all-American–owner of 

 Oil, that is. William T. Sesnon Jr., chairman of the Community Redevelopment Agency, is an oil magnate, after all. (‘Twas he who proposed the plan to finance homes for those elderly residents who had to be relocated from Bunker Hill: the City would drill on property bounded by
Oil, that is. William T. Sesnon Jr., chairman of the Community Redevelopment Agency, is an oil magnate, after all. (‘Twas he who proposed the plan to finance homes for those elderly residents who had to be relocated from Bunker Hill: the City would drill on property bounded by 
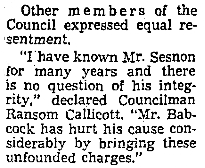 This prompted some strong words on the Chamber floor, where the next day Sesnon himself stood and said in part: “I regret the necessity of speaking but the action filed yesterday makes it unavoidable. These charges are irresponsible, malicious, vindictive and utterly false. No member of the Council ever entered into such a deal. It is an outrage that we have to face such publicity and I completely resent such statements.”
This prompted some strong words on the Chamber floor, where the next day Sesnon himself stood and said in part: “I regret the necessity of speaking but the action filed yesterday makes it unavoidable. These charges are irresponsible, malicious, vindictive and utterly false. No member of the Council ever entered into such a deal. It is an outrage that we have to face such publicity and I completely resent such statements.”

 Bunker Hill‘s final days, after its Official Designation as blighted slum, evokes not only decrepit dandified buildings like the Dome, but also its downtrodden denizens, shuffling along, infused with all the despair and longing and hopelessness you‘d expect from folks in a blighted slum. It being Official, after all.
Bunker Hill‘s final days, after its Official Designation as blighted slum, evokes not only decrepit dandified buildings like the Dome, but also its downtrodden denizens, shuffling along, infused with all the despair and longing and hopelessness you‘d expect from folks in a blighted slum. It being Official, after all.