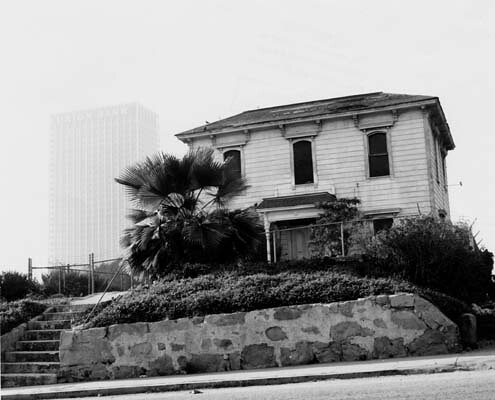
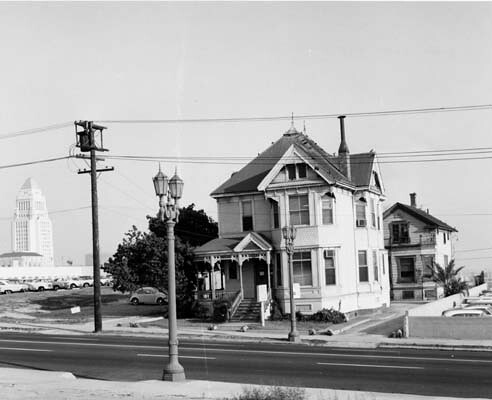
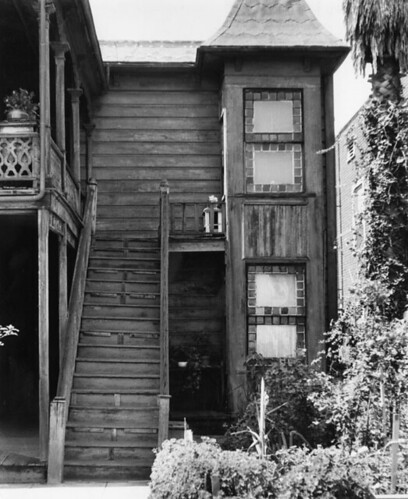
The 300 block of South Bunker Hill Avenue was supposedly one of the most picturesque in the neighborhood, if not the city. We have already taken a look at the mansions located at 315, 325, 333, and 339 South Bunker Hill Avenue. Now we are going to find out a little about the house with the address 321, also known as the Lady McDonald residence.

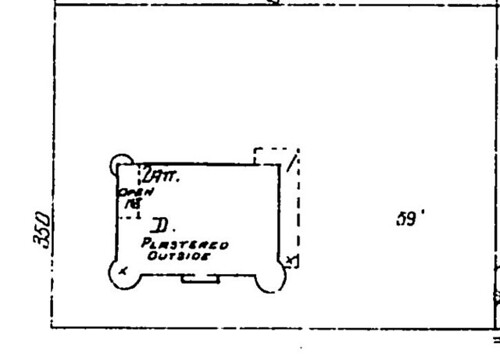
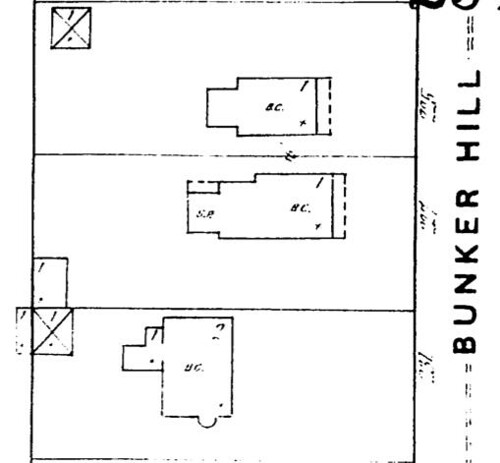
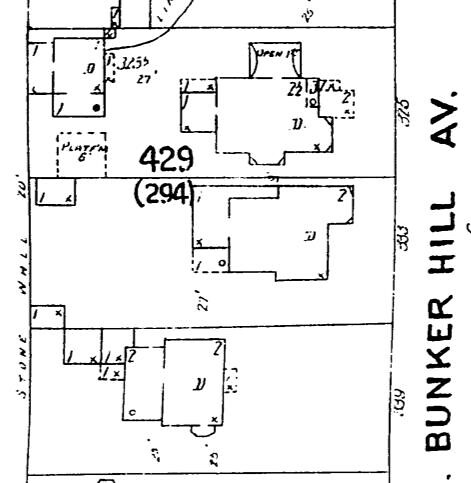
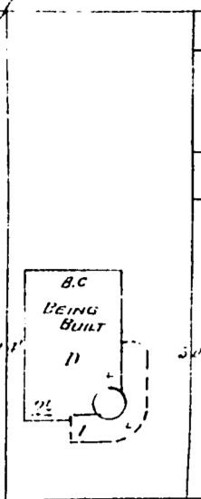
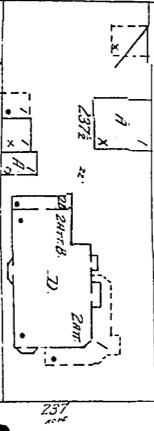
Numerous structures on the 300 block of South Bunker Hill Avenue were constructed in 1888, which may or may not be when the McDonald residence was erected. The Sanborn Fire Insurance map from 1888 (shown below) does not identify the home as “being constructed,” yet it is a mere shadow of the elaborate structure pictured on the 1894 Sanborn map (also pictured below). Please note the existence of a luxurious outhouse on the property in 1888, which by 1894 has been replaced or converted (yuck) into a guest house.

Even though neighborhood locals referred to the house for decade as the “Lady McDonald Residence,” the earliest known owner of the property was a fellow named George Ordway, whose wife served on the board of the local Y.W.C.A., and frequently entertained guests at the house. In 1892, Ordway sold the house for $10,000 to the woman who would become the mansion’s namesake.

Lady McDonald was born in Canada in 1816, and in those days was known as Frances Mitchell, daughter of a London District Court judge, and niece of noted Canadian, Egerton Ryerson. In 1838, she married the unfortunately named Donald McDonald, who was actively involved in Canadian politics and served many years as a senator. McDonald was also a shrewd investor who amassed a fortune, mainly in real estate, and he, Frances, and their fourteen children lived at the center of Toronto society in a twenty-six room mansion. Mr. McDonald died in 1879, and Frances decided to relocate with a couple of children to Los Angeles. It is unclear if being the wife of a deceased Canadian senator whose assets include a Kansas cattle ranch is qualification for a title of nobility, but when the widow McDonald rolled into town, residents always referred to her as “Lady” with a capital L.

Lady McDonald resided at the mansion with various children, grandchildren, and servants for around twenty years and lived to be nearly 100. Following the departure of the McDonalds, the inevitable happened to house at 321, and it was divided up to accommodate multiple residents. Many tenants would come and go for the next five decades, including Frank J. Giradin, a landscape impressionist who not only lived in the mansion, but used it as his art studio and held a showing of his work at 321 South Bunker Hill in 1924.
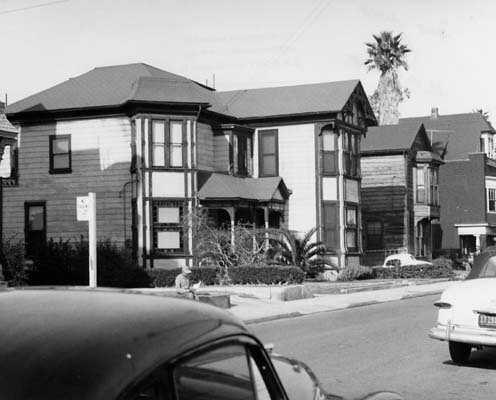

Unlike many structures on Bunker Hill, which fell into stark disrepair as the years went by, this residence seems to have been well taken care of and was noted as being in “good” condition when a WPA census was taken in 1939. By the 1960s, the condition of the property was of little consequence because the neighborhood’s days were numbered. Before the decade was over, the residences of Bunker Hill were no more, including the former home of Lady Frances McDonald.
All photos courtesy of the Los Angeles Public Library Photo Collection.